If you have Diabetes. 4 Good Reasons to get your Eye’s Examined
Diabetes is a significant public health issue in the United States, affecting millions of people across various demographics.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Approximately 34.2 million people in the U.S. have diabetes, which accounts for about 10.5% of the population.Of these, 26.9 million have been diagnosed, and 7.3 million are undiagnosed.
 Diabetes is a chronic condition that significantly impacts various organs in the body, including the eyes. High blood sugar levels can lead to damage in the eye’s blood vessels, resulting in several eye conditions collectively known as diabetic eye diseases. These conditions are a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness in adults. Understanding the relationship between diabetes and eye diseases, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the available treatments are crucial for managing these complications effectively. The eye doctors at Vision Source Insight Eye Care urge patients to seek regular eye exams as the best form of early detection against diabetic eye disease.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that significantly impacts various organs in the body, including the eyes. High blood sugar levels can lead to damage in the eye’s blood vessels, resulting in several eye conditions collectively known as diabetic eye diseases. These conditions are a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness in adults. Understanding the relationship between diabetes and eye diseases, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the available treatments are crucial for managing these complications effectively. The eye doctors at Vision Source Insight Eye Care urge patients to seek regular eye exams as the best form of early detection against diabetic eye disease.
1. Diabetic Retinopathy
Overview: Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye disease and a leading cause of blindness in adults. It occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
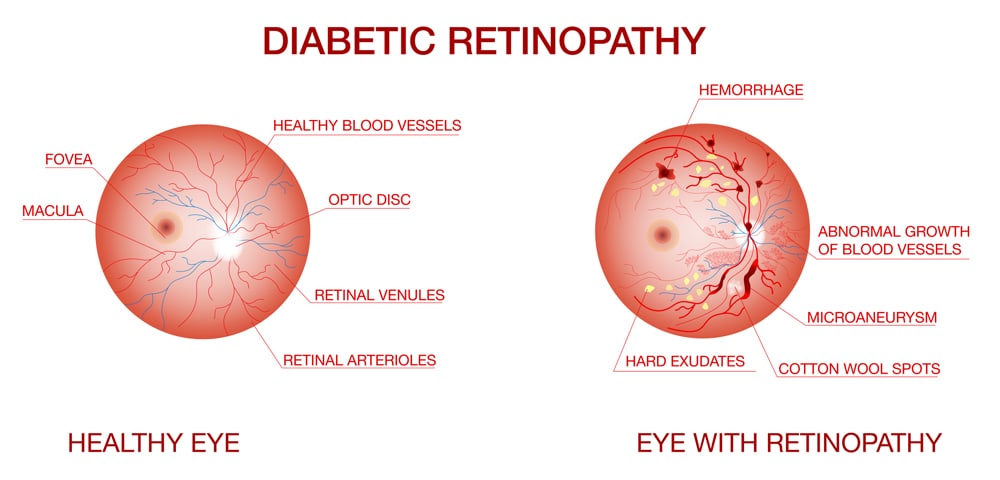 Symptoms: In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not cause any symptoms. As the condition progresses, symptoms can include:
Symptoms: In the early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not cause any symptoms. As the condition progresses, symptoms can include:
- Blurred vision
- Floaters or dark spots in the field of vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Impaired color vision
- Sudden and severe vision loss
Treatment: Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition. Options include:
- Blood Sugar Management: Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels can slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
- Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation): This treatment can seal or shrink abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
- Injections: Medications such as anti-VEGF drugs (e.g., ranibizumab, aflibercept) can be injected into the eye to reduce swelling and slow vision loss.
- Vitrectomy: In advanced cases, surgery to remove the vitreous gel and blood from leaking vessels may be necessary.
2. Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
Overview: Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a complication of diabetic retinopathy that involves swelling in the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. It occurs when fluid leaks from damaged blood vessels into the macula.
Symptoms: Symptoms of DME include:
- Blurred or wavy vision
- Color changes or distortion
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
Treatment: Treatment for DME often involves:
- Injections: Anti-VEGF (Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor) drugs can reduce swelling and improve vision.
- Laser Therapy: Focal laser treatment can seal leaking blood vessels and reduce fluid accumulation.
- Corticosteroids: Steroid injections or implants can reduce inflammation and swelling in the retina.
3. Cataracts
Overview: Cataracts are a common eye condition where the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, leading to impaired vision. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing cataracts at an earlier age than those without diabetes.
Symptoms: Symptoms of cataracts include:
- Blurred or cloudy vision
- Glare or halos around lights
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in one eye
Treatment: The primary treatment for cataracts is surgery. During cataract surgery, the cloudy lens is removed and replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This outpatient procedure is generally safe and effective, leading to significant improvements in vision.
4. Glaucoma
Overview: Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased pressure in the eye (intraocular pressure). People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing glaucoma, particularly open-angle glaucoma.
Symptoms: In the early stages, open-angle glaucoma often has no symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Loss of peripheral vision
- Tunnel vision in advanced stages
- Blurred vision
- Halos around lights
- Redness or pain in the eyes (in cases of acute angle-closure glaucoma)
Treatment: Treatment options for glaucoma aim to reduce intraocular pressure and prevent further damage to the optic nerve:
Medications: Eye drops or oral medications can reduce eye pressure.
Laser Therapy: Laser trabeculoplasty can improve drainage of fluid from the eye.
Surgery: Surgical options, such as trabeculectomy or drainage implants, can create new drainage pathways for fluid.
Preventive Measures and Management
- Regular Eye Exams: People with diabetes should have regular comprehensive eye exams at least once a year. Early detection and treatment of diabetic eye diseases are crucial to preventing vision loss. Given the large number of undiagnosed diabetes cases in the US, a regular eye exam can be best form of early detection.
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining good blood sugar control is vital in preventing or slowing the progression of diabetic eye diseases. This includes monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medications.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Management: High blood pressure and high cholesterol can exacerbate diabetic eye diseases. Managing these conditions through lifestyle changes and medications can help protect eye health.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of diabetic eye diseases and other complications. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of eye problems.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, can support overall health and reduce the risk of diabetic complications.